

Views: 45 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2024-04-12 Origin: Site
Network cable color coding refers to assigning specific colors to different wires within a network cable. This standardized approach helps ensure consistency and clarity in cable identification, facilitating easier installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance of network systems.
The importance of cable color coding cannot be overstated for maintaining an organized and efficient network infrastructure. Organizations can streamline identifying and tracing cables throughout their network environment by assigning specific colors to different cords or wires.
One of the primary benefits of cable color coding is its ability to simplify cable management tasks. When cables are color-coded according to their function, location, or type, technicians can quickly identify and distinguish between different wires, reducing the likelihood of errors and confusion during installation, maintenance, or troubleshooting procedures.
Additionally, cable color coding enhances the efficiency of cable tracing efforts. Tracing a specific cable without proper labeling or color coding can be time-consuming and labor-intensive in complex network environments with interconnected wires. However, by following a standardized color scheme, technicians can easily track the path of a cable from one end to another, facilitating faster troubleshooting and repair times.
Moreover, cable color coding helps prevent downtime by ensuring that cables are correctly connected and terminated. When cables are consistently color-coded according to industry standards or organizational guidelines, technicians can quickly verify that connections are correct, reducing the risk of connectivity issues or network failures.
Effective cable color coding promotes organization, accuracy, and efficiency in network infrastructure management. By implementing a standardized color coding system, organizations can minimize the risk of errors, streamline maintenance procedures, and ensure optimal performance and reliability of their network environment.
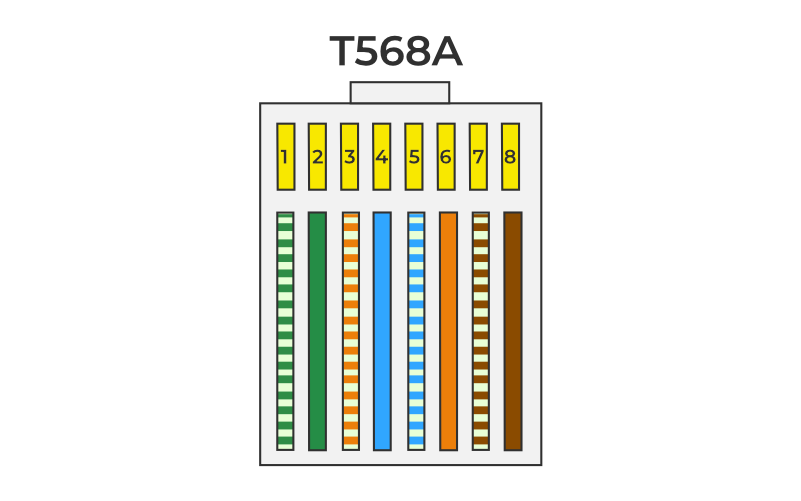
The TIA/EIA 568A and 568B standards are widely adopted for Ethernet cabling. These standards establish specific color codes for the conductors within twisted pair cables. Organizations ensure interoperability and compatibility between different network devices by adhering to these standards.
The ISO/IEC 11801 standard is a global framework for structured cabling systems. It encompasses guidelines for cable color coding to promote uniformity and consistency in network installations worldwide, irrespective of geographic location or equipment manufacturer.
In Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications, specific wire pairs may be designated for power transmission and data communication. Color coding plays a crucial role in identifying these pairs, preventing accidental damage or disruption to network connectivity. By following established color codes, technicians can ensure proper installation and maintenance of PoE systems.
Standard color coding schemes typically assign specific colors to individual conductors within network cables. For example, in Ethernet cables following the TIA/EIA 568A and 568B standards, the color coding for twisted pairs is as follows:
· Pair 1 (white/blue, blue)
· Pair 2 (white/orange, orange)
· Pair 3 (white/green, green)
· Pair 4 (white/brown, brown)
These standardized color codes facilitate easy identification and organization of cables during installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting processes. Following these color codes ensures consistency and helps technicians quickly identify the function and purpose of each wire pair within the cable.
Adhering to standardized color coding schemes offers several benefits:
· Simplifies cable identification and troubleshooting.
· Facilitates consistency and interoperability in network installations.
· Minimizes the risk of errors and confusion during cable termination and testing.
· Enhances the overall efficiency and reliability of network infrastructure.
By following established color codes, network technicians can quickly and accurately identify cables, making performing maintenance, upgrades, and repairs easier. This saves time and reduces the likelihood of errors, ensuring smooth operation and optimal network performance.
Despite the advantages of cable color coding, some common mistakes and challenges may arise, such as:
· Incorrect termination or mismatched color coding leads to connectivity issues.
· Lack of documentation or labeling makes identifying cables in densely populated environments easier.
· Non-compliance with industry standards, resulting in compatibility issues or failed inspections.
These challenges can disrupt network operations and cause delays in troubleshooting and maintenance efforts. Organizations need to address these issues by implementing proper training, documentation practices, and adherence to industry standards to ensure the effectiveness of cable color coding systems.
To ensure the effective implementation of cable color coding, consider the following best practices:
1. Follow industry standards and guidelines for cable color coding.
2. Document and label cables systematically for easy identification.
3. Regular inspections and audits are conducted to verify compliance and address any discrepancies.
4. Provide training and resources to personnel responsible for network installations and maintenance.
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can streamline their network infrastructure management processes and minimize the risk of errors and downtime associated with cable color coding.
Network cable color coding is vital in maintaining an organized and efficient network infrastructure. By following standardized color coding schemes and best practices, organizations can streamline cable identification, minimize errors, and optimize the performance and reliability of their network systems.
Cable color coding simplifies cable identification, troubleshooting, and maintenance, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency.
The TIA/EIA 568A and 568B standards specify different arrangements of wire pairs within Ethernet cables, but both ensure compatibility and interoperability.
While custom color coding is possible, it may lead to confusion and compatibility issues, so it's generally recommended to adhere to industry-standard color codes.
Document cable color coding schemes in network diagrams, labeling systems, or documentation manuals to ensure consistency and ease of reference.
Cable testers and labeling tools can help verify cable connections and maintain accurate documentation of color coding schemes.